Who is EDITO for?

The short answer is - EDITO is for everyone!
The European Digital Twin Ocean is being co-created by many individuals and communities – including ocean researchers, data scientists, modellers, and national and international ocean projects and initiatives. But you don’t have to know how to code to contribute to, and benefit from, the core infrastructure platform of the European Digital Twin Ocean.
EDITO is being designed to engage a wide variety of users who will add further value to the European Digital Twin Ocean community, including policy- and decision- makers, citizen scientists, blue economy stakeholders, activists, citizen scientists and the general public. Everyone has a role to play, and everyone benefits from each other’s contributions.
To suit different user profiles, EDITO has three service offerings: Create, Contribute, and Explore. Explore these users below, plus some real-world examples of how each can harness the power of the European Digital Twin Ocean.
Creators are ocean researchers, data scientists, modellers and/or developers who create (design and deploy) services on the EDITO platform. This includes building and running digital twins, leveraging supercomputing tools, or running new ocean simulations.
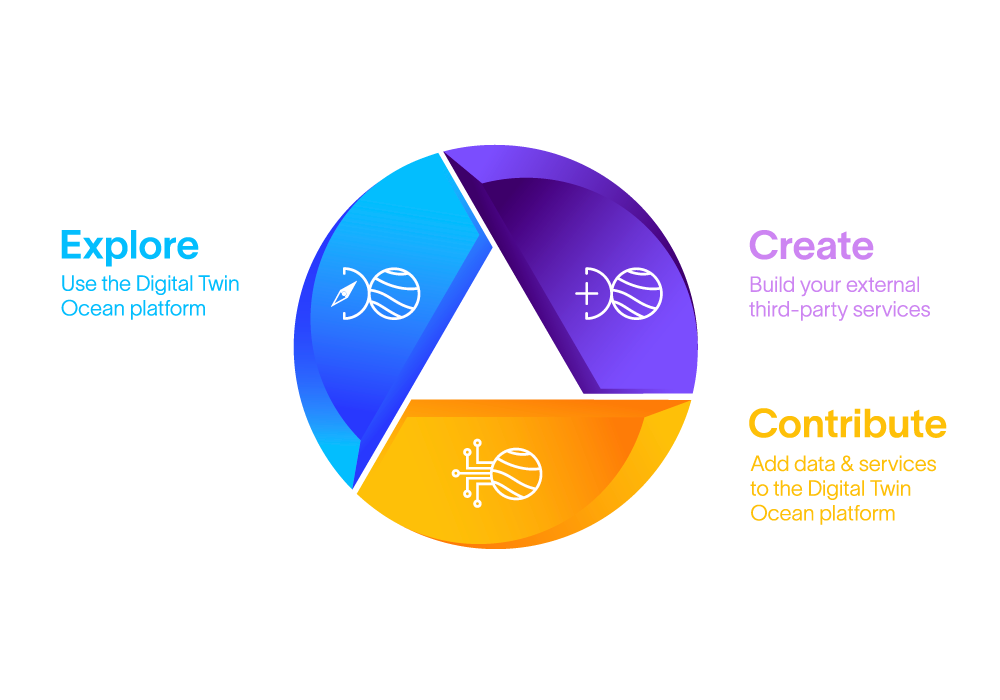
Contributors are experts representing organisations, institutes, or private companies that are working on specific research projects and would like to share their developments, tools, or data on the EDITO platform.
Explorers are end-users who do not necessarily have scientific or technical expertise, but can use the EDITO platform to learn more about marine environments and explore different scenarios. This user group includes policy- and decision-makers, blue economy stakeholders, activists, citizen scientists, and wider society.

Watch the video and see what EDITO has in store for you!

EDITO: The public infrastructure of the European Digital Twin Ocean




This work is funded by the European Union under grant agreement no. 101227771. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Research Executive Agency (REA). Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Privacy policy | Cookie policy | Website by Seascape Belgium